How Does Experiential Education Work?
HOW DOES EE WORK?
LEARNING CYCLES
Experiential education (EE) is philosophically grounded in experiential learning (EL), which recognizes that reflection on lived experience is critical to learning. While many authors have posited complex models to explain the ongoing cycle of EL, a simple one is presented below.
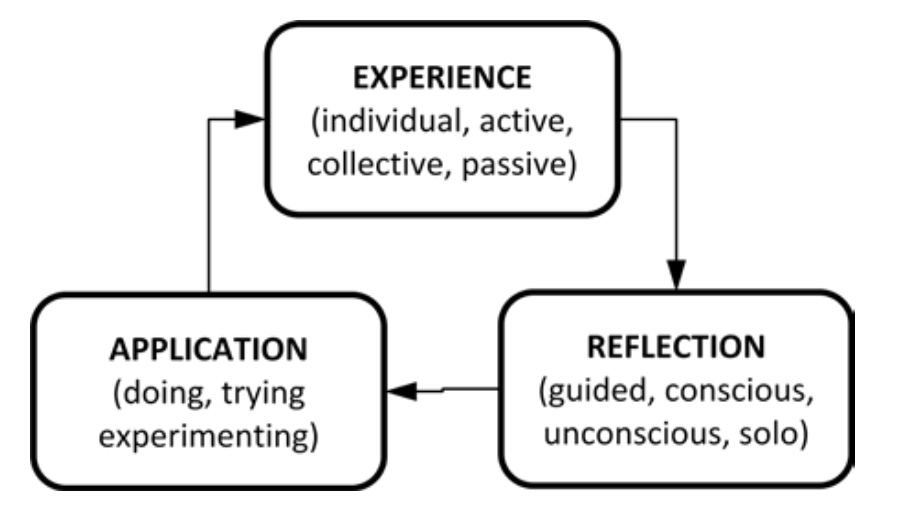
These three steps have been broken up once each to provide four, five, and six step cycles as discussed in “further resources.” For example, the last step of application can be divided into integration and continuation (and so on).
CYCLE STEPS
Experience encompasses all of one’s senses, perceptions, and beliefs. It includes everything people engage in and how they engage with the world. It stimulates the mind, body and spirit, usually simultaneously. It is encountered while participating in activities, sitting quietly in calm contemplation, and the moments in between. All of human learning is experience-based, but it becomes experiential when reflection is added.
Reflection means to consider the meaning of an experience by careful thought. Reflection can occur in partner dialogues, in group discussions, and in solo contemplations. It can be conscious or unconscious. However, EL seeks to bring intentional awareness to mindfully considering experiences and what these mean to clients. One value of intentional reflection is avoiding a negative element of EL that Dewey called “miseducative.” Biases or stereotypes are examples of how reflections can become mis-educative.
Application uses learning generated during reflection for clients to behave differently in the next experience that will be newly reflected on. It is an opportunity to test the trustworthiness, validity, reliability, and truth of recent learning.
CYCLE FACILITATION
Facilitating reflection accelerates and cements learning. It creates an intentional awareness of the need to change and the desire to transform.
Sophisticated methods of facilitating reflection through EL are discussed in “further resources.” However, one fundamental tool to employ first is asking three questions to mirror the EL cycle.
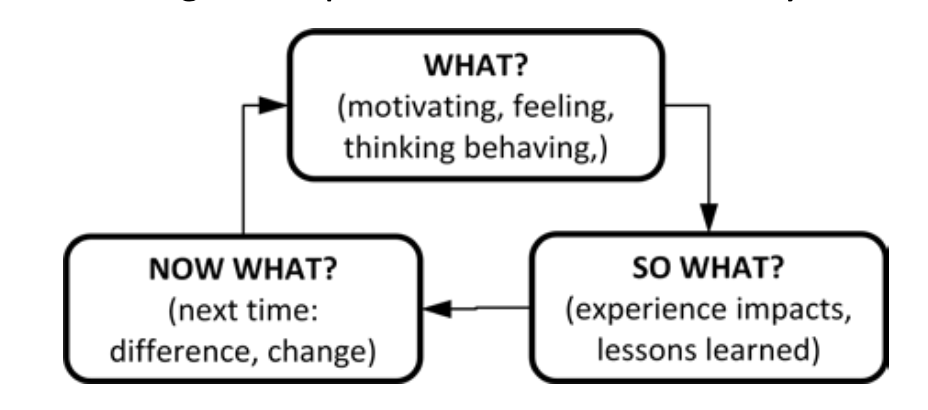
What? What happened? What was sensed, felt or thought? The first question assists clients to understand an experience’s content or context.
So what? So what did this impact do to the group, task, or you? So what was learned? The second question helps clients to decipher the meaning of their experience.
Now what? Now what will you do differently? The third question aids clients to envision how they can practice another way to make change.
AUTHORS: Christian Itin & Simon Priest | Published in 2022
FURTHER RESOURCES
Allison, P. & Wurdinger, S. (2005). Understanding the power, promise, and peril of the experiential learning process. Teacher Education and Practice, 18(4), 386-399.
Beard, C. & Wilson. J. P. (2002). The Power of Experiential Learning: A Handbook for Trainers and Educators. Kogan Page Limited.
Breunig, M. (2005). Turning experiential education and critical pedagogy theory into praxis. Journal for Experiential Education, 28(2), 106-122.
EBLS (Aug 3, 2019). 8 Things to know about the Experiential Learning Cycle. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v74nRbWSNqk
Itin, C. M. (1999). Reasserting the philosophy of experiential education as a vehicle for change in the 21st century. Journal of Experiential Education, 22(2). 91-98
Kolb, D. A. (2015). Experiential Learning: Experience as the Source of Learning and Development, 2nd Edition. FT Press.
Smith, T. E., & Knapp, C., Seaman, J. & Pace, S. (2011; 2010;). Experiential education and learning by experience. In Smith T. E., Knapp C. E. (Eds.), Sourcebook of Experiential Education: Key Thinkers and their Contributions. Routledge, 1-11.
TEDxLakelandUniversity (Mar 20, 2019). Engaged Experiential Education - Jess Lambrecht. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qlhHPsiNxCM
Via Experientia: the International Academy of Experiential Education (2009). The Philosophy and Theory of Experiential Education. https://www.viaexperientia.net/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Introductionto-the-Philosophy-and-Theory-of-Experiential-Education-_ViaEx.pdf
What is "experiential learning"? https://www.edb.gov.hk/attachment/tc/curriculumdevelopment/kla/pshe/references-and-resources/ethics-and-religiousstudies/experiential_learning_2.pdf
